- Home >
- Product >
- Excavator >
- Wheel excavator >
- View Details
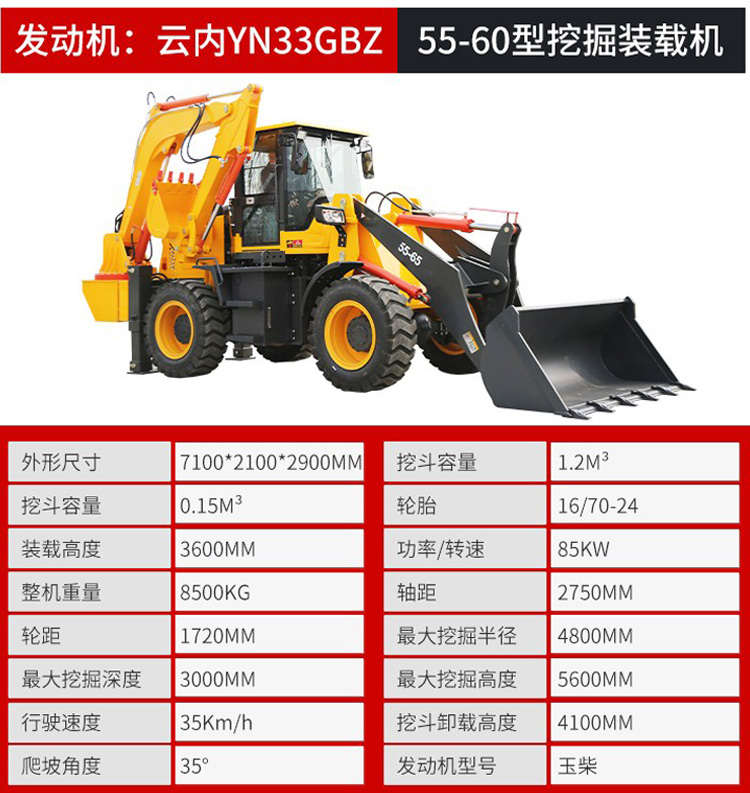
Factory outlet HK-80 Wheel excavator
Modern wheel excavators are equipped with advanced technology such as GPS, digital monitoring systems, and automated controls. These features enhance operational efficiency, precision, and safety. Some models also offer hybrid engines, reducing fuel consumption and environmental impact.
- ZHUOXIN
- shandong.china
- TT, Paypal, Credit card, Western union
- +86-15163766288
- A typical wheeled excavator comprises a two-part articulated arm, a rotating cab, and a wheeled undercarriage. The primary components include a boom, stick, and bucket, which are hydraulically operated. These machines come in various sizes and capacities, tailored to diverse operational needs.
Description

Wheeled excavators, often regarded as versatile and mobile construction equipment, have become increasingly popular in various construction, mining, and urban engineering projects. Unlike their tracked counterparts, wheeled excavators offer enhanced mobility, reduced ground damage, and improved efficiency on hard surfaces.

Design and Features:
A typical wheeled excavator comprises a two-part articulated arm, a rotating cab, and a wheeled undercarriage. The primary components include a boom, stick, and bucket, which are hydraulically operated. These machines come in various sizes and capacities, tailored to diverse operational needs.

Mobility and Versatility:
The defining feature of wheeled excavators is their rubber tires, which provide significant advantages in terms of mobility. They can easily travel between job sites without the need for additional transport equipment, making them ideal for urban projects or jobs requiring frequent relocation. Their tires also cause less damage to paved surfaces compared to tracks.

Applications:
Wheeled excavators are commonly used for digging, trenching, lifting, and material handling. Their adaptability makes them suitable for various tasks, including road construction, utility work, landscaping, and demolition. Attachments like hammers, grapples, and augers further enhance their versatility.
Technological Advancements:
Modern wheeled excavators incorporate advanced technology for enhanced performance and operator comfort. Features such as GPS, advanced hydraulics, and computerized control systems allow for precise operations. Many models also include eco-friendly engines that reduce emissions and fuel consumption.

Mobility and Versatility
One of the key advantages of wheel excavators is their superior mobility. They can travel at higher speeds than track excavators, allowing for efficient movement between and within job sites. This mobility also reduces the need for additional transport equipment. Furthermore, they cause less damage to paved roads, making them suitable for urban environments.

Applications
Wheel excavators are used in a wide range of applications, from digging trenches and holes to demolition, material handling, and river dredging. They are particularly useful in urban construction projects, road maintenance, and landscaping tasks. Their ability to quickly move between sites makes them ideal for projects requiring high flexibility.

Design Characteristics
Wheel-based Mobility: The primary feature of wheeled excavators is their wheel-based mobility, allowing for smoother movement on concrete and asphalt, reducing damage to these surfaces compared to track-based systems.
Structural Components: A typical wheeled excavator consists of a rotating cab, an articulated arm, a bucket, and a set of four to eight wheels. The cabin offers comfort and safety for the operator with advanced control systems.
Attachment Versatility: Similar to tracked excavators, wheeled variants can operate with various attachments, including different types of buckets, breakers, and even augers, enhancing their utility in diverse operations.
Operational Advantages
Speed and Efficiency: One of the main advantages of wheeled excavators is their ability to move quickly between job sites without the need for additional transportation. This mobility saves time and increases efficiency in projects.
Urban and Road Work: These excavators are particularly advantageous in urban settings and for road works, where their mobility and reduced impact on paved surfaces are crucial.
Environmental Considerations: Wheeled excavators tend to have a lower ground pressure which results in less soil compaction and environmental impact, particularly in sensitive areas.

Design and Features:
A typical wheeled excavator comprises a two-part articulated arm, a rotating cab, and a wheeled undercarriage. The primary components include a boom, stick, and bucket, which are hydraulically operated. These machines come in various sizes and capacities, tailored to diverse operational needs.

Mobility and Versatility:
The defining feature of wheeled excavators is their rubber tires, which provide significant advantages in terms of mobility. They can easily travel between job sites without the need for additional transport equipment, making them ideal for urban projects or jobs requiring frequent relocation. Their tires also cause less damage to paved surfaces compared to tracks.

Applications:
Wheeled excavators are commonly used for digging, trenching, lifting, and material handling. Their adaptability makes them suitable for various tasks, including road construction, utility work, landscaping, and demolition. Attachments like hammers, grapples, and augers further enhance their versatility.

Technological Advancements:
Modern wheeled excavators incorporate advanced technology for enhanced performance and operator comfort. Features such as GPS, advanced hydraulics, and computerized control systems allow for precise operations. Many models also include eco-friendly engines that reduce emissions and fuel consumption.

Mobility and Versatility
One of the key advantages of wheel excavators is their superior mobility. They can travel at higher speeds than track excavators, allowing for efficient movement between and within job sites. This mobility also reduces the need for additional transport equipment. Furthermore, they cause less damage to paved roads, making them suitable for urban environments.

Applications
Wheel excavators are used in a wide range of applications, from digging trenches and holes to demolition, material handling, and river dredging. They are particularly useful in urban construction projects, road maintenance, and landscaping tasks. Their ability to quickly move between sites makes them ideal for projects requiring high flexibility.

Design Characteristics
Wheel-based Mobility: The primary feature of wheeled excavators is their wheel-based mobility, allowing for smoother movement on concrete and asphalt, reducing damage to these surfaces compared to track-based systems.
Structural Components: A typical wheeled excavator consists of a rotating cab, an articulated arm, a bucket, and a set of four to eight wheels. The cabin offers comfort and safety for the operator with advanced control systems.
Attachment Versatility: Similar to tracked excavators, wheeled variants can operate with various attachments, including different types of buckets, breakers, and even augers, enhancing their utility in diverse operations.
Operational Advantages
Speed and Efficiency: One of the main advantages of wheeled excavators is their ability to move quickly between job sites without the need for additional transportation. This mobility saves time and increases efficiency in projects.
Urban and Road Work: These excavators are particularly advantageous in urban settings and for road works, where their mobility and reduced impact on paved surfaces are crucial.
Environmental Considerations: Wheeled excavators tend to have a lower ground pressure which results in less soil compaction and environmental impact, particularly in sensitive areas.
Tags
Get the latest price? We'll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)























